Condition的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
| public class ConditionWait implements Runnable{
private Lock lock;
private Condition condition;
public ConditionWait(Lock lock, Condition condition) {
this.lock = lock;
this.condition = condition;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("begin condition-wait");
try {
lock.lock();
condition.await();
System.out.println("end condition-wait");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public class ConditionSignal implements Runnable{
private Lock lock;
private Condition condition;
public ConditionSignal(Lock lock, Condition condition) {
this.lock = lock;
this.condition = condition;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("begin condition-signal");
try {
lock.lock();
condition.signal();
System.out.println("end condition-signal");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| public class ConditionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
ConditionWait wait = new ConditionWait(lock,condition);
ConditionSignal signal = new ConditionSignal(lock,condition);
new Thread(wait).start();
new Thread(signal).start();
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
}
|
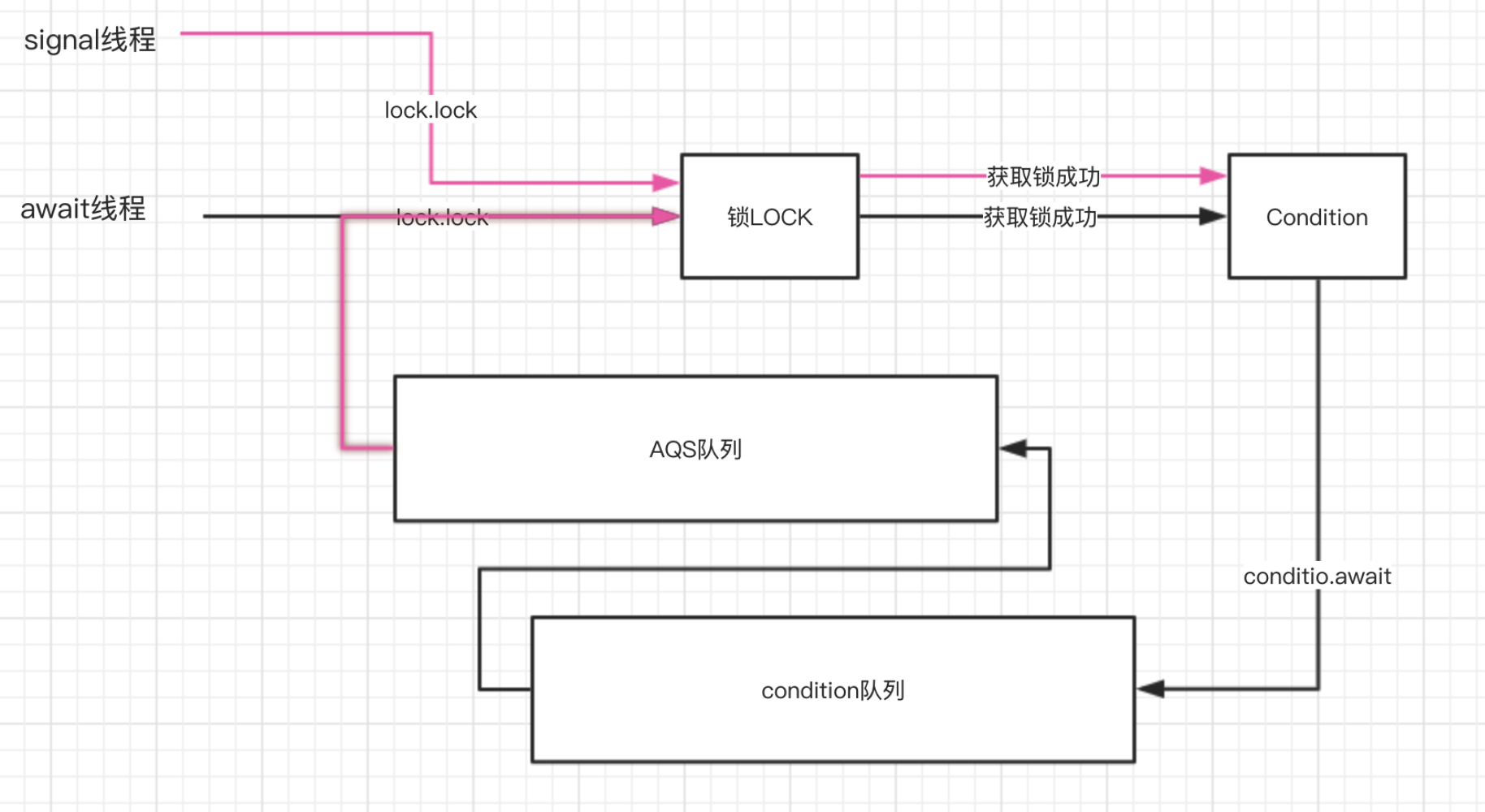
condition底层的底层实现是维护了一个等待队列,当调用condition.await的时候加入到condition队列,阻塞当前线程。当另外的线程调用signal或者signalALL方法,把等待队列的节点追加到同步队列中,重新抢夺cpu资源。
CountDownLatch的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(3);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("子线程执行任务:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
countDownLatch.countDown();
},"thread"+i).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("主线程继续执行任务啦");
}
|
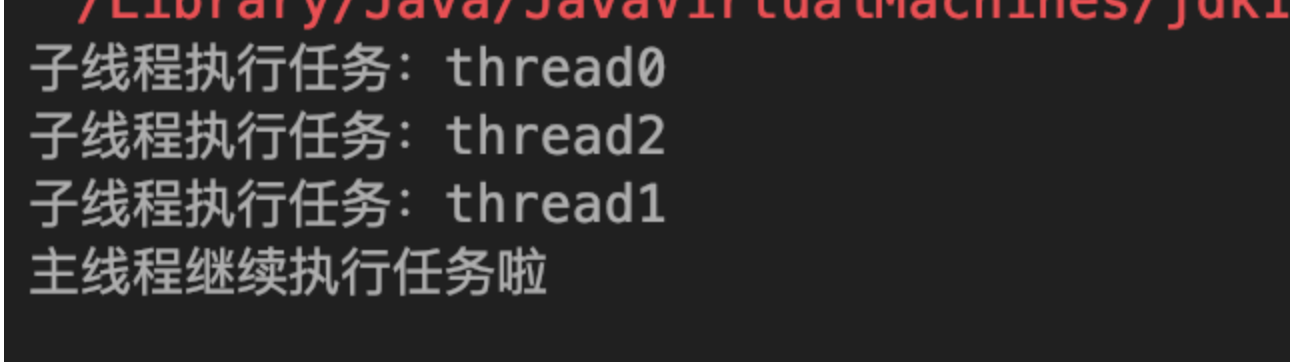
定义一个计数器state,通过CountDownLatch的构造方法传入,调用CountDownLatch.await方法时会阻塞线程。其他线程每执行一次CountDownLatch.countDown方法,state会减一,当state等于0的时候,原阻塞线程会被唤醒
Semaphore的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| public class SemaphoreDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(5);
for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
new Car(i+1,semaphore).start();
}
}
static class Car extends Thread{
private int num;
private Semaphore semaphore;
public Car(int num, Semaphore semaphore) {
this.num = num;
this.semaphore = semaphore;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
semaphore.acquire();
System.out.println("第"+num+"量车抢占车位");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
System.out.println("第"+num+"量车走了");
semaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
|
这个例子演示了车俩进入停车场的时候,停车场的车位是有限的,我们预设一个数量,当数量达到的时候,后面进来的车俩必须等待其他车俩释放车位。
Semaphore用于限流,Semaphore定义了一个令牌数permits,当每一个调用semaphore.acquire()的时候permits都会减1,当permits数量=0的时候,调用线程会阻塞,等待其他线程release。
CyclicBarrier的使用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class DataInputThread extends Thread{
private CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier;
public DataInputThread(CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier) {
this.cyclicBarrier = cyclicBarrier;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+" 开始导入数据");
try {
cyclicBarrier.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| public class DataCleanThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("等待其他线程全部传输数据完毕,开始清理数据");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public class CyclicBarrierDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier = new CyclicBarrier(3,new DataCleanThread());
for (int i =0 ;i<3;i++){
new DataInputThread(cyclicBarrier).start();
}
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
}
}
|

上面的例子演示了数据清理线程等待子线程导入完数据之后才开始执行程序。
CyclicBarrier跟CountDownLatch用法差不多,但是CyclicBarrier可以重复使用,每一次配套的子线程和等待线程执行完之后,又会重置计数器重复试用。



